Save time and money with planning-first shipping optimization.
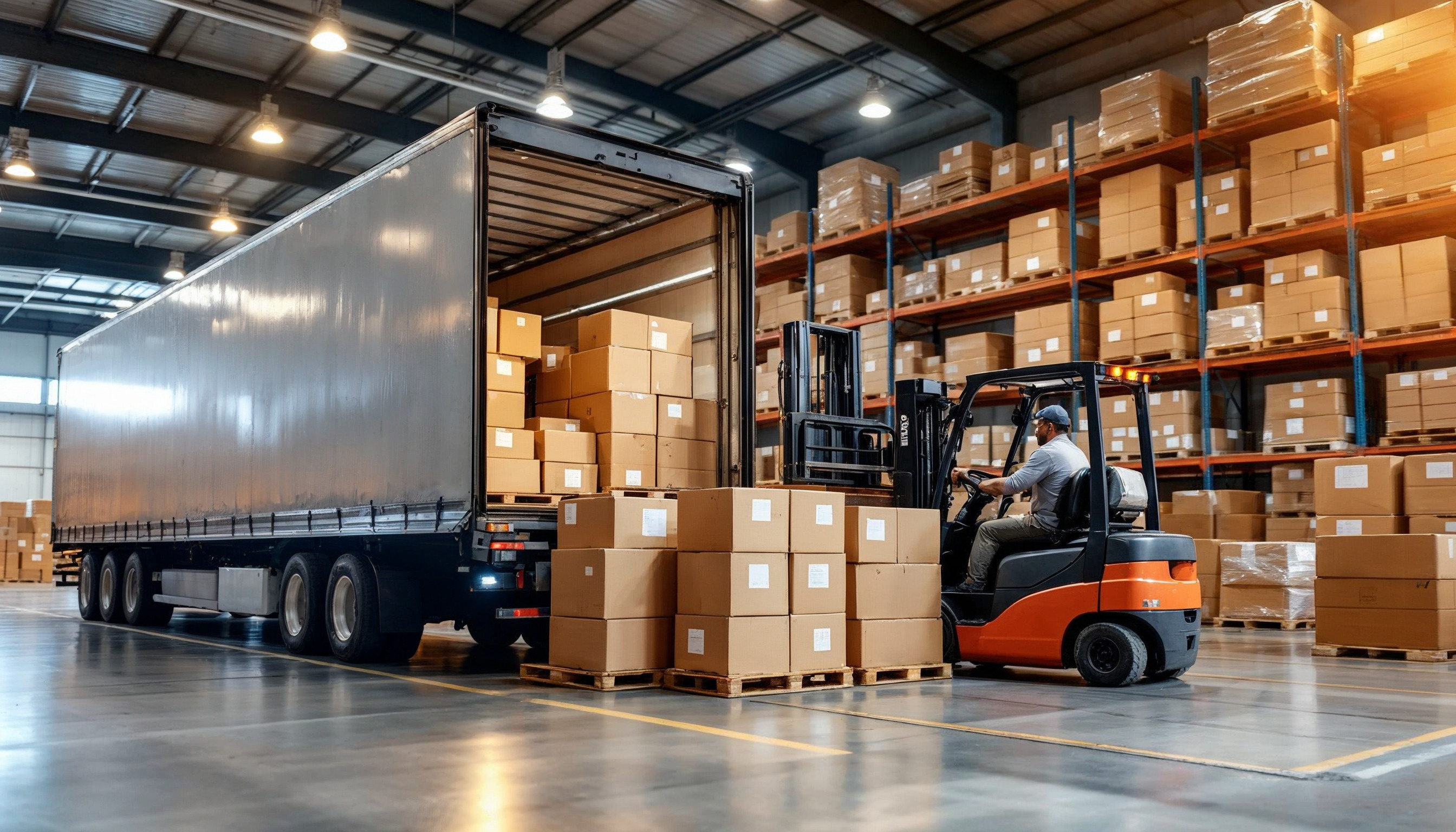
CONTACT USIf you or your business are looking for a way to ship goods that are too heavy for traditional shipping options but would not entirely fill a trailer, you should consider less-than-truckload (LTL) freight.
With LTL shipping, carriers consider the weight, size, packaging and special handling needs of goods to calculate the risk and cost of shipping. While this process tends to be more complex compared to full truckload (FTL) shipping, it offers greater flexibility and cost savings.
That said, determining if LTL shipping is right for your business and choosing the right carrier will depend on a number of factors.
What Is LTL?
Less-than-truckload shipping is a means of transporting small freight or cargo that does not require or is not capable of filling a full truck. While it is not limited to businesses, LTL is most commonly used by companies who want to ship small amounts of cargo frequently.
Key requirements and specifications of LTL shipping include:
- LTL freight combines multiple shipments into one trailer.
- LTL freight is used for cargo weighing between 150 pounds and 20,000 pounds.
- LTL shipping is recommended for cargo that is 6 pallets or less.
- LTL freight is often slower than FTL, as it requires multiple stops.
- LTL shipping requires more handling, as cargo may need to be moved as each shipment is dropped off.
This method of shipping helps businesses optimize shipping costs by consolidating multiple shipments into one trailer. With this method, transportation costs are shared with other organizations, who fill the remaining space within a truck.
LTL shipping is usually a cheaper option than its counterpart, full truckload shipping, in which an entire truck is used for a single shipment. When shipping with FTL, the customer must pay for the entire truck's space, even if there are portions not used. You can learn more in our discussion on LTL vs FTL.
The Basics of Less-Than-Truckload (LTL)
While shipping a full truckload may provide faster deliveries and more predictable costs, using scheduled, frequent LTL shipments instead can mitigate risks of overstock. This has the added benefit of reducing waste while keeping supply chains steady, which may incentivize LTL carriers to offer discounts — thus, optimizing costs.
It is also worth noting that different LTL carriers offer specialized services that may benefit your organization.
For instance, some LTL freight shippers operate under the premise of "assembly service," in which a group of small shipments are combined to make a larger shipment. This grouped cargo can then be shipped to an individual location or multiple customers. Assembly services can not only reduce costs but also reduce risk of damage, especially when the goods are smaller, uniform in shape, or easily stowable.
Knowing the size, scope and special services an LTL carrier offers is crucial when choosing a cargo shipper. Employing a company that understands the importance of logistics coordination and making use of shipment management platforms will further help to make your LTL shipping and handling processes more efficient and cost effective.
How Less-Than-Truckload (LTL) Works
LTL carriers rely on a hub-and-spoke model, where local terminals (spokes) connect to a series of central hubs, through which freight is routed through. Using this model helps shipping coordinators optimize delivery times and reduce costs by having the ability to choose the most optimal delivery routes.
These same spokes and hubs follow a set of industry standards set by organizations like the National Motor Freight Traffic Association (NMFTA). As such, LTL cargo must adhere to and be measured by certain factors, including:
- Weight: LTL freight ranges from 150-10,000 pounds; although, some carriers allow up to 15,000 pounds, depending on shape and packaging.
- Size: LTL cargo consists of 6 or fewer pallets.
Packaging: LTL carriers rate packages and goods by how “stowable” they are, which allows them to better calculate available space in a truck as well as safety risk. - Specialized Handling: LTL freight rates are also determined based on any special handling, like manual labor, lift gates, cranes, safety equipment or temperature-control.
Using these metrics, LTL carriers are able to apply specified ratings to cargo to ensure it is delivered safely and on time.
Less-Than-Truckload and the E-Commerce Era
The steady rise of e-commerce has led to the need for affordable and reliable shipping. More and more, companies are relying on LTL carriers to keep products close to customers and remain competitive with online retailers and larger corporations that have their own delivery and transportation arms.
LTL freight is excellent for digital storefronts who need a flexible, fast and affordable shipping solution. LTL carriers can benefit e-commerce players by offering discounts for smaller, more frequent loads and creating an inventory distribution mechanism that can rapidly scale with ease.
Optimizing shipping costs through methods like split shipping and assembly service, as well as reducing breakage through pallets and wrapping, can help carriers pass savings on to the shipper, making them a more attractive option.
Using an LTL carrier helps small business owners and smaller retailers skip the initial and ongoing investment — and logistics nightmare of — offering their own delivery services.
Pros and Cons of Less-Than-Truckload (LTL)
Understanding the risks and benefits of LTL shipping can help you decide if an LTL carrier is the right option for your business needs.
It should be noted that some of the drawbacks of LTL shipments can be mitigated through the use of shipping management platforms, which remove some of the associated planning, logistics and regulatory challenges.
Pros:
- Cost savings through shared truck space and the opportunity to negotiate special discounts for volume and frequency.
- Regulated pricing by industry organizations such as the NMFTA, helping ensure fair shipping rates.
- Greater flexibility and a wider range of special services to ensure cargo is handled and delivered accordingly.
Cons:
- Longer delivery times due to more drop-off locations.
- More complicated planning and logistics since trailers carry multiple shipments from different customers.
- Greater risk of damaged goods due to increased handling.
Benefits of LTL Shipping for Over-the-Road Shippers
In addition to cost efficiency and increased flexibility, businesses that utilize over-the-road LTL shipping contribute to sustainability efforts because it reduces the number of vehicles on the road, which slashes fuel usage and emissions. In addition, shared freight optimizes space and bolsters corporate environmental initiatives and regulatory compliance.
Can I Ship Anywhere Using LTL?
LTL shipping can support national and even cross-border shipping to countries like Mexico and Canada. With that said, there may be certain regulations, requirements, and/or restrictions you should discuss with your LTL carrier when planning routes and shipments.
In particular, Cross-border transportation comes with its own regulatory and documentation requirements. And remote areas or "off-the-grid" locations may be inaccessible due to safety or infrastructure limitations.
For LTL carriers that have limited or restricted coverage, it is possible for them to extend their coverage area through the use of partner carriers and alternative transport companies. These shipping alternative partners specialize in delivering to areas like Alaska or Hawaii or regions suffering from natural disasters.
What Else Do I Need to Know About LTL Shipping?
Below, we cover some additional considerations businesses that are new to LTL shipping need to know. This includes:
- Paperwork requirements
- Freight protection strategies
- LTL pricing
- Shipment and tracking visibility
Paperwork Requirements
Paperwork and proper documentation are crucial to ensuring goods are not delayed or damaged and arrive on time. This is especially true for cross-border and international deliveries, where special documentation, such as Area of Origin and customs documents, are required.
Of particular importance is an accurate, error-free and complete Bill of Lading (BOL), which is essentially a detailed list of goods being shipped. It is to the consignor of goods by the LTL carrier and should include the following shipment information:
- Shipper and consignee information.
- Carrier or freight forwarder information.
- Date of shipment.
- Description of goods.
- Date of shipment.
- HS codes.
- Purchase order.
- Terms of shipping and freight payment terms.
- Declaration of value.
- Special instructions for handling.
Signature and date.
Freight Protection
Due to the nature of LTL shipping and consolidated shipments, it is important to ensure cargo is properly packaged. Since your freight will share space with other goods and is often stacked and co-loaded, using suggested packaging best practices can help protect not only your commodities, but other items in the trailer.
Ways to strengthen the integrity of your shipment, make it more stowable, and easier to stack:
Include using shrink wrapping on pallets.
Provide packing foam or peanuts inside boxes.
Use uniform packaging.
Consider custom packaging options like formed Styrofoam or corrugated boxes.
Label items as fragile, temperature-sensitive or hazardous accordingly.
When thinking of packing materials, keep environmental factors in mind as well, such as road conditions, weather, humidity and
temperature.
LTL Pricing
LTL freight pricing can be hard to determine, as it partially depends on market rates. However, there are several factors that can help you estimate freight rates and avoid unexpected fees.
In general, LTL rates vary based on factors like:
- Weight: The total weight of the shipment.
Dimensions: The total size of the cargo being shipped. - Freight class: A designation, ranging from 50 - 500, that is based on density, handling, stowability and liability.
- Special services: The types of special services required to ship or handle the freight.
Tracking and Visibility
Tracking shipments can seem like a daunting task, but fortunately most LTL carriers provide shipment tracking through online portals and shipment tracking platforms. These shipping tracking tools have common features that make it easy for users to gain visibility into their shipments and manage certain aspects of the shipping process. This includes:- Pickup scheduling.
- Rate quotes.
- Claims filing.
- Route optimization.
- Shipment tracking.
Weather and Delays
Weather and road conditions can be difficult to predict, so it is important to always monitor shipments and routes to avoid any potential delays or risks to cargo. These occurrences are rare but still need to be taken into consideration when planning shipments.
Key Players Involved in LTL Shipping
There are three main players that work together to ensure shipments occur as efficiently and safely as possible. They are: carriers, freight brokers, and 3PLs.
- Carriers: LTL carriers are the people who ship and handle the cargo and freight of a shipment.
- Freight Brokers: Freight brokers are the middleman between the carrier and the company hiring the carrier responsible for communicating between the two companies to ensure goods arrive safely and on-time.
- 3PLs: A 3PL is a third-party logistics company used by carriers to help with supply chain services, including shipping, storing and handling
Typical Timeline for LTL Shipments
While each shipment will vary, the typical delivery time for an LTL shipment is two to seven days. That being said, this is a general rule, and a number of factors can affect this timeline, including:
- Pickup and delivery location.
- Carrier schedules.
- Services required and service level.
- Weather and road conditions.
Always discuss delivery schedules with your LTL carrier and set realistic expectations of delivery times to avoid added costs and inventory issues.
Choosing the Right LTL Carrier
Now that you understand how less than truckload shipping works, we can discuss how to choose the right LTL carrier.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an LTL Carrier
While choosing the right LTL carrier will largely come down to your own business needs and shipping requirements, there are some key factors to consider when choosing an LTL carrier, such as:
- Service Quality: Read reviews to see what past customers have to say about the quality of service the carrier provided.
- Customer Support: Discuss the customer support options available in the event something goes wrong during handling and transportation. Check online reviews to see how customer support responded during negative situations.
- Pricing Structure: Review and compare rates of multiple LTL and FTL carriers to ensure you’re getting the best price for what you need.
- Coverage: Ensure the LTL carrier can ship to where you need them to.
Insurance: Evaluate the carrier’s insurance options. - Specialty Services and Equipment: Check that the carrier offers the services or equipment you need for your shipments.
While shipping rates and total cost are important, make sure to consider other items on our list to get an overall picture of the total value the LTL carrier brings to the table.
Importance of Carrier Reliability and Network Coverage
The reliability of a carrier is probably the most important factor to consider when choosing a shipping carrier. The key is to find a company that offers consistent delivery and service; has excellent customer satisfaction; and can help you with logistics planning, route optimization and costs.
Choosing a company with a broad network coverage that can ship to a large variety of regions can help your business scale up during booming business and protect you from losses due to shipping delays and disruptions.
Role of Technology in Optimizing LTL Carrier Selection
A good LTL carrier will employ a string suite of shipping tools and provide online portals and shipment planning platforms to help shippers optimize and track shipments.
Other tools, like electronic document interchanges (EDI) are important because they facilitate the exchange of important documents, such as shipping notices, shipping documents and invoices.
Shipment tracking tools help shippers avoid delays or lost shipments, and shipping analytic software can provide key insights into shipping processes and past shipments to make more informed business decisions that can affect ROI.
The use of up-to-date technology is the sign of a good, reliable LTL carrier.
Practical Tips for Effective LTL Shipping
In the next section we cover some practical tips for effective LTL shipping, including best practices for packaging, how to consolidate shipments for maximum efficiency and how to utilize shipment software for LTL shipment tracking.
Best Practices for Packaging and Labeling LTL Shipments
When packaging items for freight cargo, it is important to use containers that are uniform in size and shape if possible. Make sure boxes are securely packed and cushioning with styrofoam filler or other material. Boxes should be tightly sealed at all openings to avoid spillage or breakdowns. Remember that boxes will be stacked and need to support weight and pressure during transport and handling.
To avoid damage or loss, ensure all items are properly labeled and contain information such as content, durability, shipper and consignee information, and special handling instructions. Barcode or QR labels can help mitigate user errors and provide consistency.
How to Consolidate Shipments to Maximize Efficiency
Consolidating multiple orders into one shipment helps reduce shipping cost per unit and improves delivery speed in several ways:
Consolidated shipping helps split the cost of trailer space.
LTL carriers are more likely to offer discounts to shippers who ship frequently or consistently, as they tend to favor volume.
To consolidate, consider using a distribution center to store and manage goods, and coordinate with suppliers to group shipments and avoid the need for multiple deliveries.
Utilizing Technology and Software for LTL Shipment Tracking
Tracking platforms, whether provided by a carrier or 3PL, can provide an additional layer of visibility into shipments that help shippers avoid delays, make proactive and informed business decisions, and avoid surprises. In the event of a disaster or delay, shipment tracking platforms also help improve response time and protect the bottom line.
When using shipment tracking tools, always set up automated alerts to monitor key milestones, such as arrival points, redirected routes, and pickup and drop-offs.
Stress-Free Small Cargo Shipping With Planimatik
There are many factors involved when planning shipping logistics, whether your company is shipping locally, nationally or cross-border. Planimatik's shipping management solutions can help transportation coordinators manage small cargo shipping efficiently and without hassle.Some of the key features of Planimatik's shipping management platform include:
- Quoting: Shippers can input specific details for accurate and transparent rates and costs customized to their needs.
- Scheduling: Shippers can optimize LTL shipments, increasing efficiency and reducing potential downtime.
- Save quotes: Shippers can save quotes for up to four days, providing stability in a market where rates change frequently.
- Back office assistance: Shippers have access to tailored and specific load details for optimized rates and can receive expert guidance to address concerns, ensuring easy and efficient LTL shipments.
- Integrations: Shippers can easily add their common carriers and integrate seamlessly with their preferred carriers to ensure they get the best rates from their trusted providers.
Ready to learn more about Planimatik’s shipment management tools? Ask for a demonstration of our digital freight platform.
FAQs
Below are some answers to frequently asked questions about less than truckload shipping and LTL freight shipments.
What is considered less than truckload?
Cargo weighing between 150-15,000 pounds and making up six or fewer pallets is considered less than truckload or LTL freight.
What's the difference between LTL and FTL?
LTL combines multiple shipments into one truck, while FTL uses one shipment to fill an entire truck.
Who pays for LTL shipping?
For a typical prepaid shipment, each shipper pays the carrier for their portion of the load in the trailer. However, this can vary depending on the terms of sale; "freight collect" shipments are paid for by the receiver (consignee).
How does LTL shipping work?
LTL shipping works by consolidating multiple shipments from multiple shippers into one truckload. In this way, shipping costs are split and optimized to maximize savings.



.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)



 READ MORE
READ MORE

.png?width=464&height=512&name=13-cta-img-01%20(2).png)